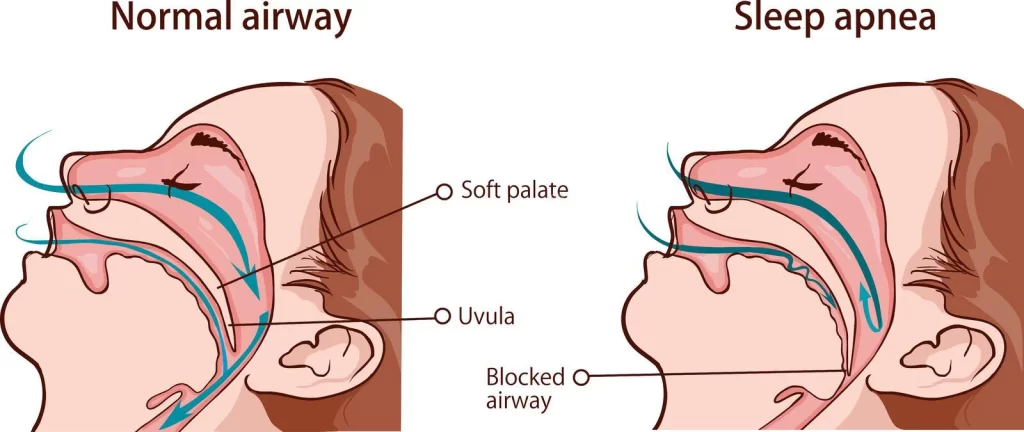
What is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder that happens when a person’s breathing is interrupted during sleep. People with untreated sleep apnea stop breathing repeatedly during their sleep, sometimes hundreds of times during the night.
.
What are the different types of sleep apnea?
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the more common of the two. Obstructive sleep apnea occurs as repetitive episodes of complete or partial upper airway blockage during sleep. Breathing usually resumes with a loud gasp or body jerk. These episodes can interfere with sound sleep, reduce the flow of oxygen to vital organs, and cause heart rhythm irregularities
In Central Sleep Apnea (CSA), the airway is not blocked but the brain fails to signal the muscles to breathe due to instability in the respiratory control center
Signs & Symptoms
Often the first signs of sleep apnea are recognized not by the patient, but by the bed partner. Many of those affected have no sleep complaints. The most common signs and symptoms include:
Snoring
Daytime sleepiness or fatigue
Restlessness during sleep
Frequent night-time awakenings
Sudden awakenings with a sensation of gasping or choking
Dry mouth or sore throat upon awakening
Cognitive impairment, such as trouble concentrating, forgetfulness or irritability
Snoring
Daytime sleepiness or fatigue
Restlessness during sleep
Frequent night-time awakenings
Sudden awakenings with a sensation of gasping or choking
Dry mouth or sore throat upon awakening
Cognitive impairment, such as trouble concentrating, forgetfulness or irritability
Mood disturbances (depression or anxiety)
Mood disturbances (depression or anxiety)
Night sweats
Frequent night-time urination
Sexual dysfunction
Headaches
Night sweats
Frequent night-time urination
Sexual dysfunction
Headaches
What are the Complications that Sleep Apnea will lead to?
Sleep apnea is a serious medical condition. Complications can include:
-
Daytime fatigue
-
High blood pressure or heart problems.
-
Type 2 diabetes
-
Metabolic syndrome
-
Liver problems
What are the causes of Sleep Apnea?
- Obstructive sleep apnea is caused by a blockage of the airway, usually when the soft tissue in the rear of the throat collapses during sleep.
- Central sleep apnea is usually observed in patients with central nervous system dysfunction, such as following a stroke or in patients with neuromuscular diseases. It is also common in patients with heart failure and other forms of heart, kidney or lung disease.
How to diagnose Sleep Apnea?
Your doctor may make an evaluation based on your signs and symptoms and a sleep history, which you can provide with help from someone who shares your bed or your household, if possible.
Tests to detect sleep apnea include:
- Nocturnal polysomnography: During this test, you’re hooked up to equipment that monitors your heart, lung and brain activity, breathing patterns, arm and leg movements, and blood oxygen levels while you sleep.
- Home sleep tests: Your doctor might provide you with simplified tests to be used at home to diagnose sleep apnea.
How to treat Sleep Apnea?
Treatment aims to normalize breathing during sleep and address any underlying health problems. The options will depend on the cause and severity of symptoms.
Lifestyle changes
Lifestyle modifications are essential to normalizing breathing and are critical first steps in treatment.
They include:
- following a heart-healthy diet
- developing healthy sleeping habits
- limiting alcohol consumption
- quitting smoking
- managing weight
- sleeping on the side
Other options
Other treatment options include:
- Airway pressure therapy: This is the main treatment for sleep apnea. It keeps the airway open by gently providing a constant stream of positive pressure air through a mask.
- Surgery
- Medication: Some drugs may help but should only be used after consultation with a sleep specialist.
What are the risk factors of Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea can affect anyone, even children. But certain factors increase your risk. Factors that increase the risk of sleep apnea include:
Excess weight
Neck circumference. People with thicker necks might have narrower airways.
A narrowed airway
Smoking
Medical conditions like Congestive heart failure, High blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes and Parkinson's disease

